Thermal Camera Applications Industrial
Industrial Thermal Camera Applications
Carry out non-contact temperature analysis of critical machinery and electrical equipment without carrying out extensive testing procedures during machinery downtime. Thermal cameras used in this industry are able to increase productivity, decrease machinery downtime making repairs and prevent problems from becoming damaging long before they get the chance.
Industrial environments thrive because of two things; the workforce, and the machinery they use. Workers are needed to keep machinery in good working order and to interact with functions, while machinery increases productivity significantly and ensures that the working environment is profitable, constantly moving and safe for those around it. As this reliance in machinery increases within industrial environments so to does the need to constantly maintain delicate machinery, piping and energy sources to ensure that the industrial environment remains in correct working order.
There are several ways to test machinery and the general environment within industry, but perhaps one of the most growing methods of testing is to carry out thermal surveys. Either automated or carried out using handheld units, thermal technology used within industry has a number of benefits over other testing methods which are outlined further below.
But how do thermal cameras actually work? In order to understand how these intutive devices benefit industrial applications, you first need to understand a little about the science behind these systems.
Thermal Cameras - An Explanation
What is a thermal imaging camera? Well - to put it in the simplest way possible - thermal cameras are able to take pictures of our environment and measure the temperature of thousands of points within the image. In more technical terms, a thermal imaging system measures infrared (IR), a totally invisible part of the light spectrum that exists around us constantly, converts the detected emissivity of objects into an image and displays it as a heatmap of different temperatures.
The technical explanation, while it may initially sound confusing, is relatively easy to understand. Everything around us - be it your computer, your own body or even an ice cube - outputs some form of IR radiation, usually as heat. This output is known as the emissivity of the object and because our eyes are not adapted to do so, it is impossible for humans to view this distribution normally. A thermal camera, via the use of complex technology, is able to detect this heat being distributed as IR, carries out calculations based on detected temperature levels and captures it almost instantly as an image that shows the detected temperature as different colours.
This makes it significantly easier to measure temperature over an area without the need to use infrared or digital thermometers (or other similar equipment) and also allows the user to carry out completely non-contact temperature measurements from a distance.
The heatmap that is displayed on each captured thermal image differs greatly depending on which model of thermal imaging system is used to capture the image in the first place. To recap, here's exactly what thermal sensitivity and emissivity mean.
Thermal Sensitivity
This refers to how sensitive the camera is to shifts in temperature. The higher the thermal sensitivity is, the more accurate the overall reading taken using the thermal camera will be.
Emissivity
IR radiation given off as heat by an object. Hotter objects generally have higher emissivity due to them putting out excessive amounts of IR radiation.
How is Thermal Technology Useful In Piping?
The applications of thermal technology used in industrial environments are vast. These systems are perhaps one of the most useful objects that can be used as part of any ongoing maintenance program and their ability to capture accurate temperature readings at a distance makes it easy to spot problems, take corrective action and maintain employee safety during dangerous maintenance procedures.
Imagine, for example, you need to measure piping due to a suspected problem. It's impossible to get too near the pipes as they are superheated, but shutting them down might let the problem slowly disappear and make it harder to locate. So how do you go about testing the piping? Do you shut it down and risk inaccurate measurements, or do you risk sending in an employee near to superheated pipes that could cause significant burns and other problems?
The answer is neither: you use a thermal imaging camera instead.
By using a thermal camera the use can stand at a safe distance from the pipe, capture an image easily and then study it afterwards to see how heat is distributed within the pipe. If irregular heat patterns are detected this could mean breakdown of piping integrity, problems inside the pipe or many other potential problems. The user can use the thermal image as a reference point, power down the system and then study the affected parts of the pipe once cooling procedures have taken place.
This method of testing can be used to detect leakages in pumps, pipes and vales, insulation breakdowns and pipe blockages.
A quick, easy method of problem prevention.
Diagnosing Electrical Problems
Since a significant amount of industrial machinery relies of the power electricity provides, breakdowns and loss of efficiency in components can incur costly running costs or make systems unsafe for operation. Established methods of testing electrical components - such as using relevant testing equipment such as multimeters - are fine in general practice, but when you've got a massive machine built of countless components, how do you quickly isolate which one is causing the problem? Is a section of wire frayed and not letting electricity flow naturally? Has a fuse blown in the system? It's impossible to tell at a glance and may require extensive testing of each component to pinpoint exactly which one is causing all the trouble.
Again, a thermal camera can speed up this process significantly. Whereas testing each component could be costly, time-consuming and extremely difficult to perform, capturing a thermal image of the electrical components and analysing which one(s) are outputting excessive amounts of IR radiation simply be looking at how hot the components appear on the thermograph.
Again, this process enables the user to carry out testing when the system is active and is much more likely to be able to determine problems.
Thermal cameras are now also commonly used in analysing the electrical components inside electrical panels without the need to open them up. This is accomplished by the use of special IR window, unique glass panes that allow a thermal camera to see through them (conventional glass reflects back IR radiation, making it impossible to see through when looked at using a thermal imaging camera). This makes testing electrical panels significantly easier and - again - allows the panel to be powered on during testing and makes it easy to tell at a glance if any components are outputting an excessive amount of heat.
So why make life more difficult for yourself? Simply buy a thermal camera and see exactly how your maintenance program will be enhanced before your very eyes.
High Voltage Testing
Although electricity is always a significant danger, this is never truer than in high voltage applications such as substations. Breakdowns in high voltage components can cause everything from power outages to electrical shocks and fires, so it is important to regularly test high voltage installations to make sure they are running exactly as intended.
Problems generally arise in high voltage installations because of heat. They are designed when first implemented to generate the least amount of heat possible, but factors such as corrosion, loosening of parts or the effects of weather can cause a direct rise in electrical resistance, thus causing the high voltage system to output more heat. This reduces the efficiency of the unit, can cause brakdowns and can cause a significant rise in the price of running the unit due to excessive energy output as heat. If you leave it long enough, this heat can even cause components to melt.
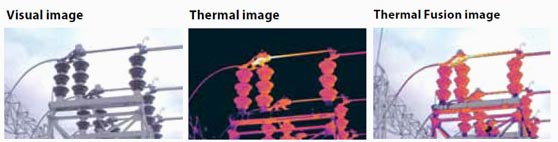
The inspection of a substation reveals overheated components.
A thermal camera is able to safely test high voltage installations from a distance in order to get a grasp of overheating components. It can be used to:
- Detect oxidation of high voltage switches
- Detect overheated connections
- Detect incorrectly secured connections
- Check for insular defects
Like standard electrical testing applications, high voltage equipment can also be tested when under load by using a thermal camera. This makes it much easier to check high voltage substations, switchgear, transformers and outdoor circuit breakers for accuracy and makes spotting problems significantly easier.
Industrial Thermal Camera Downloads
The following is a list of application stores associated with thermal camera usage within industrial areas.
Recommended Industrial Thermal Cameras
Many thermal imaging systems are general purpose devices, making them ideal for use in industrial applications. Since thermal cameras are designed with durability in mind, they are also highly resistant to the effects of high impact environments such as industry and are generally protected against knocks, bumps, drops, water and dust damage.
The following is a quick list of thermal cameras recommended for use in industrial applications:
*Products with Thermal Imaging:
Armor 27T pro,Armor 25T Pro,Armor 25T, Power Armor 18T Ultra, Power Armor 19T, Power Armor 18T, Armor 11T 5G, Armor 9.














































